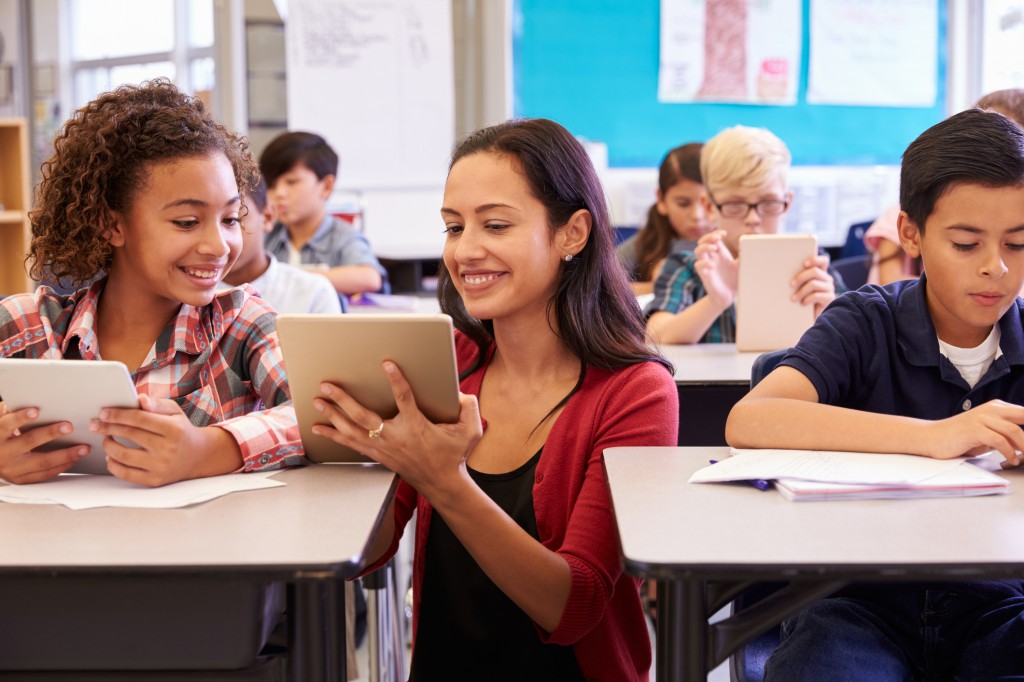
In a diverse classroom, educators need to recognise that students have different learning styles. Some students thrive in visually stimulating environments, while others may retain information better through auditory or kinesthetic means. To create an inclusive and effective learning experience, teachers must understand these various learning styles and adapt their instructional strategies accordingly.
Visual Learners:
Visual learners grasp information best when presented in a visual format. They rely on visual aids such as charts, graphs, diagrams, and images to understand and retain concepts. To cater to visual learners:
a. Utilise visual aids: Incorporate visually appealing materials such as slideshows, videos, and posters to supplement lessons. These aids provide a clear visual representation of information, ensuring a deeper understanding.
b. Encourage note-taking: Encourage visual learners to take detailed notes during lectures or discussions. This enables them to visually organise and review information later.
c. Use colour coding: Incorporate colour-coded materials or visual markers to help visual learners organise and categorise information effectively.
Auditory Learners:
Auditory learners are most receptive to information through sound, tone, and language. They comprehend and retain knowledge better through verbal instructions, lectures, and discussions. To engage auditory learners:
a. Encourage discussions and debates: Create opportunities for students to engage in discussions, debates, and group activities that involve verbal interaction. This allows auditory learners to process information by listening and expressing their thoughts orally.
b. Utilise audio recordings: Provide recorded lectures or educational podcasts that auditory learners can listen to repeatedly, reinforcing their understanding of the subject matter.
c. Incorporate rhymes and mnemonics: Utilise rhymes, songs, or mnemonic devices to help auditory learners remember key information. These auditory cues create associations that aid in retention.
Kinesthetic Learners:
Kinesthetic learners thrive when they can physically engage with the material. They learn best through hands-on experiences and movement. To address the needs of kinesthetic learners:
a. Incorporate tactile materials: Utilise manipulatives, hands-on experiments, or models to help kinesthetic learners engage with the subject matter actively.
b. Encourage movement: Incorporate activities that involve movement, such as role-plays, simulations, or physical demonstrations. This allows kinesthetic learners to embody the concepts they are learning.
c. Provide opportunities for practical application: Allow kinesthetic learners to apply their knowledge through real-life scenarios or projects. This will enable them to directly experience the practical implications of what they have learned.
By understanding and catering to the diverse learning styles of visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners in the classroom, educators can create an inclusive and effective learning environment. By incorporating visual aids, encouraging discussions, providing hands-on experiences, and adapting instructional strategies, teachers can ensure that all students have the opportunity to learn and succeed. Remember, every student is unique, and by embracing different learning styles, we can unlock their full potential and make learning a truly enriching experience for all.